THE LIFEBLOOD OF THE BUSINESS…
WORKING CAPITAL
Finance is necessary for the establishment of the business and to carry out the day-to-day business operations. Capital is required to purchase the plant, land, building, furniture, machinery, etc, which are called as fixed assets. Investment on fixed assets represents the part of the firm’s capital, and funds are blocked on a long term and fixed basis, so it is called fixed capital.
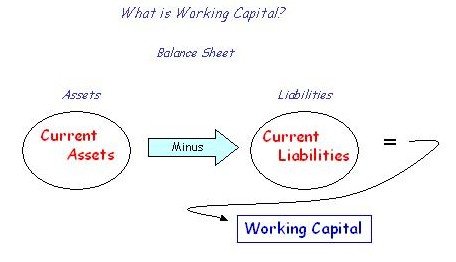
Funds are necessary for the purchase of raw materials, payment of salaries or wages and to fulfill the routine expenses is called as working capital which is necessary for financing cash, purchase of inventories, debtors and for securities, which are called as current assets. Such an investment can be converted into cash and again cash can be invested to get current assets. Thus working capital is a short term and circulating investment. The estimation of working capital is done by the difference between current assets and current liabilities.
Classification of working capital
Working capital is classified in two ways, on the basis of concept and time permanency.
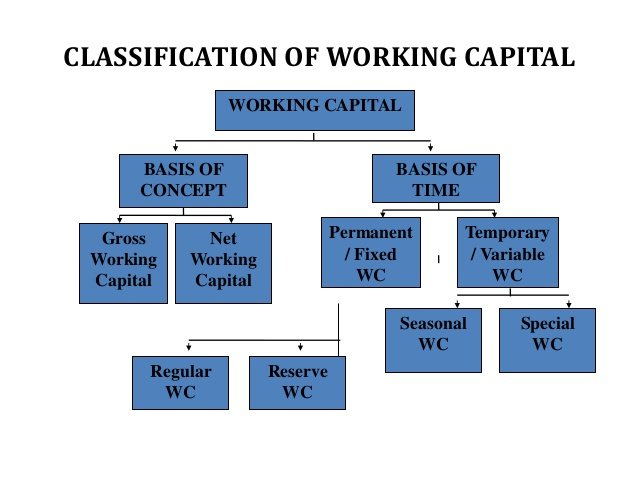
On the basis of concept
On the basis of concept net and gross working capital are the two concepts of working capital.
Gross working capital:
The funds invested in the current assets of the business firm are called as gross working capital and these current assets can be changed into money within a short duration i.e. twelve months.
Examples of current assets are cash in hand or bank balance, accounts or bills receivables, short-term loans, advances, sundry debtors, temporary investments of surplus funds, accrued incomes, inventories of stocks i.e raw materials, stores and spares, work in process, and finished goods, and prepaid expenses, etc.
Net working capital:
Net working capital is used to measure the short-term liquidity of a business firm, depending on a firm’s current assets and it’s current liabilities, its current financial status can be determined. While taking the difference if the current assets are more, then the position is said to be positive, when the current liability exceeds then it will be negative.
Examples of current liabilities are bills payable, outstanding expenses, sundry creditors or accounts Payable, short term loans, bank overdraft, provision for taxation, advances, deposits, and dividends payable, etc.
On the basis of time
On the basis of time, working capital is classified into permanent or fixed and temporary or variable short-term capitals.
Permanent working capital:
To perform the business activities, minimum current assets are required and it is known as permanent working capital or fixed working capital. A business has to maintain a minimum level of cash, raw materials, semi-finished goods and finished products to run the business profitably. Fixed working capital is further classified into, regular and reserve circulating capitals. The capital which is required for the flow of current assets is known as regular working capital and the additional amount which is used to face the uncertainty is called as reserve working capital.
Temporary working capital:
It is the amount necessary to fulfill the seasonal requirements and some special needs such as to conduct marketing campaigns and research etc. Temporary working capital is used to fulfill the short term requirements.
Objectives of working capital
To purchase the raw materials
To pay wages, salaries
To fulfill other day-to-day expenses
To fulfill overhead cost such as fuel, power, and office expenses, etc.
To meet marketing expenses, such as packing, and promoting, etc.
To provide credit facilities
To maintain the raw materials, work-in-progress, and finished goods, etc.
Importance of working capital
Working capital is essential to maintain the smooth functioning of a business firm. Without an adequate amount of working capital, a firm may not be successful. The main advantages of working capital are as follows.

Smooth running of a business
An adequate amount of working capital facilitates uninterrupted production which helps in smooth functioning of the business.
Easy loans
Good credit standings, an adequate amount of working capital and high solvency make possible to get the loans on favorable terms and conditions.
Goodwill
Regular and prompt payments is a great task to the business firms, adequate working capital enables a business to fulfill this task and helps in creating good will.
Cash discounts
If a firm has sufficient amount of working capital enables bulk purchases, it makes possible to get discounts which highly reduces the cost of production.
Continuous supply of raw materials
Regular and continuous supply of raw materials are necessary for the continuous production. Adequate working capital facilitates production without breaks; it highly reduces cost and time.
Regular payments of wages and salaries
If an organization has sufficient amounts of working capital then there is a possibility of regular payment of wages and salaries and it motivates the employees and workers which in turn improves employee’s efficiency; it greatly reduces the wastage and maximizes the profits.
Bulk purchases
During favorable conditions and to increase the production there arise a need for cash; adequate amount of working capital facilitates bulk purchases.
Ability to face crisis
Reserve working capital enables a firm to face uncertain market conditions.
Quick return on Investment
Sufficient working capital helps in smooth running of the business which in turn maximizes profits and quick return on investments.
Factors determining the working capital requirements
Factors such as the nature and size of business, production policy, operations, the length of the production cycle, the state of economic situation and the rate of stock turnover etc determine the requirement of the working capital.
Nature of the business:
Nature of the business decides the working capital requirements such as for some firms less working capital is necessary for regular business operations. Trading firms and manufacturing undertakings require more investment in inventories, cash, and receivables, so for these firms a large amount of working capital is necessary.
Scale of operations:
The size of the business or scale of operations directly influences the working capital requirements. In some cases, economies of scale are applicable and result in the reduction of cost and working capital as well. However, in the case of small firms also working capital increases due to the overhead charges, and due to the various economic disadvantages.
Working capital cycle:

Funds are necessary for the purchase of raw materials, payment of salaries or wages and to fulfill the routine expenses is called as working capital which is necessary for financing cash, purchase of inventories, debtors and for securities, which are called as current assets. Such an investment can be converted into cash and again cash can be invested to get current assets. Thus working capital is a short term and circulating investment. Usually longer the operating cycle, larger will be the working capital requirement.
Credit policy:
Depending on the credit policy of the business firm, working capital requirements varies. Allowing credits may increase the sales and profits, however, during the initial stages of the policy implementation higher working capital is required.




